网络上的两个程序通过一个双向的通信连接实现数据的交换,这个连接的一端称为一个socket。
一直想在尝试两台设备之间互相连接,通信,交互的功能。了解到Socket,很有意思。基本可以实现我的设想,甚至可以多台设备互联,不清楚成熟的物联网又是通过什么什么进行互联?
我的初步目标是用 Android 手机控制小车,不过小车估计自己是做不来了,硬件能力都荒废了。
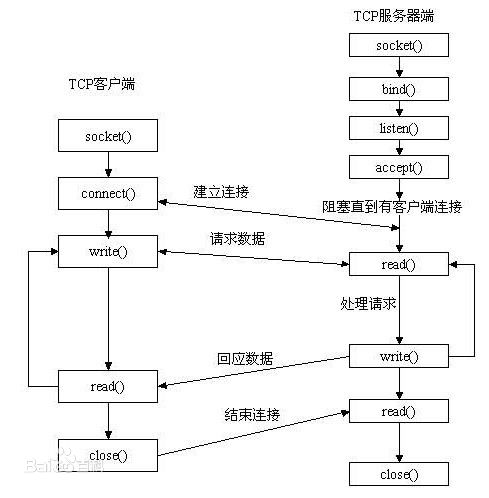
再熟悉一下 Socket 的工作机制:
本人的软件开发相关的项目、知识笔记
网络上的两个程序通过一个双向的通信连接实现数据的交换,这个连接的一端称为一个socket。
一直想在尝试两台设备之间互相连接,通信,交互的功能。了解到Socket,很有意思。基本可以实现我的设想,甚至可以多台设备互联,不清楚成熟的物联网又是通过什么什么进行互联?
我的初步目标是用 Android 手机控制小车,不过小车估计自己是做不来了,硬件能力都荒废了。
再熟悉一下 Socket 的工作机制:

最近在折腾Web相关的项目,Web相关知识从零开始。不过,相比嵌入式驱动开发,Web项目的入门门槛还算是低的。这也是我这种懒人想死守嵌入式驱动开发的原因,毕竟门槛高,竞争比较少。
这次的Web练手项目,主要是根据用户提供的关键字,搜索出相应的题目以及答案。
项目的整个架构由我策划,基于Spring,整合Lucene搜索引擎,中文识别用IKAnalyzer,服务器用Ubuntu + tomcat。
历时两周,硬件+软件+知识储备都是从零开始,也算是对Web项目开发有了初步的认识。
同时新上手了Intellij idea这个主流的IDE,毕竟从零开始嘛,开发工具肯定用主流的,快捷键切换为Eclipse的即可。
也对Maven基于项目对象模型(POM)有所了解,主要用来简化项目的构建工作。当然刚接触时被一堆配置信息搞得晕头转向,特别是网上没有源的库还要自己手动配置整理。但一旦配置完成后,POM文件的可重用性,真的很方便,而且最终的项目打包时,库的集成方面的工作也是无忧解决。大赞。
新平板产品量产过程中,工厂反映有1%的触摸屏出现无法正常工作。拿到不良的触摸屏后,通过分析系统启动的 log,发现触摸屏驱动已经加载,但是 probe 函数中打印无法找到 0x38 设备。0x38 设备就是 ft5x06 的设备从地址,证明 I2C 通讯没有成功。但是奇怪的是,这些不良的触摸屏在上一款硬件雷同的平板上可以正常工作。
I2C 通信不成功的原因无非以下几点:
因为我们上一款平板的触摸屏驱动是由 RK 直接提供的,而且我们也量产1年时间,没有发现类似的问题。出问题的这款平板硬件跟上一版本的雷同,软件驱动也是一样的,所以认为软件驱动应该没什么问题,电气性的问题概率会大一点。
尽管如此,我还是重新检查了一遍触摸屏驱动,调整 I2C 速率,重新烧录后发现还是老样子。
决定去硬件组看看。硬件的同事用示波器观察了 I2C 的通信波形,发现出现了中间电平。数字电路不是只有高电平,低电平,1和0吗?怎么出来了一个中间电平了。什么是中间电平?例如芯片规格规定高电平是高于2.4V,电平低于0.4V,如果出现了1.4V的话,那就是中间电平了。
出现中间电平,可能是因为触摸屏内阻比较大,分压过大,造成低电平下不来。
可以通过修改上拉电阻,提高上拉电阻的分压比例,降低触摸屏内阻的分压比例,达到低电平降下来的效果。换10K上拉电阻,老样子,再换…直到换了一个50K的电阻之后,低电平果然就下来了,I2C 通信波形也很正常,触摸屏工作正常!但是50K上拉电阻的情况下,其它本来正常的触摸屏的波形就不是很好。这个方案不完美。
然后就考虑通过调整 CPU I2C 端口驱动电流来实现上拉电阻提高分压比例的方法,RK3188的 I2C 端口默认是 2 ma, 通过软件配置寄存器,将驱动电流调整为 4ma 后,波形正常了,不良的触摸屏也可以正常使用了。而且对其他正常的触摸屏也没有影响。
问题解决!
手写控件相关文章:http://kevinems.com/tag/%E6%89%8B%E5%86%99
本人在好记星平板电脑 N818S 上开发的原笔迹手写控件,压感,笔锋都实现了,笔迹保存,还原,删除,放大,缩小,旋转,移动功能也实现了,控件的API简单易用,可以说是一个比较完善的控件了,并集成到 Framework,小有成就感啊。
当初需求统计,分析是就认定是一个相对复杂的控件,所以前期做了不少工作,后期编码实现的时候相对还算比较顺利。
这是第一次真正意义上遵循了标准的软件开发流程,开发效率果然提高不少。科学的开发方法,事半功倍。
流程大概:
平台:好记星 N818S,Android 4.2,汉王电磁屏,电磁笔
笔触效果:钢笔,铅笔,马克笔,毛笔
效果图:
一个终端培训师的作品~~~

AlarmManager 的使用是 Android 初学者比学掌握的,网上教程一箩筐,这里就不罗嗦了。
这里有一个比较好的教程 Android – Creating an Alarm with AlarmManager
本文的重点是如何把休眠的机器唤醒,点亮屏幕并显示相关的界面。
但是值得注意的就是,AlarmManager 唤醒系统后,跑完相关程序后,又会继续休眠下去。
如果你需要像我一样,唤醒屏幕去显示闹钟界面,那就要加上 WakeLock。
WakeLock 相关源码:
private PowerManager.WakeLock wl;
...
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
PowerManager pm = (PowerManager) getSystemService(Context.POWER_SERVICE);
wl = pm.newWakeLock(PowerManager.FULL_WAKE_LOCK, "My Tag");
wl.acquire();
...
... //The rest of the onCreate() is still the same (for now)
}
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
wl.release();
}
// 值得注意的是,WakeLock 必须 release, 具体位置可以自己安排
// 别忘了加上权限 uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WAKE_LOCK";
更多可以参考这里: Starting Activity from Sleeping Device
序列化 (Serialization) 的相关知识可以参考相关的百科,这里只要是学习 android.graphics.Path 的序列化。
工作中有需求要保存绘制的 paths, 这个时候就需要用到对象的序列化的功能,但是 Android 上没有对 Path 做序列化的工作,所以只能自己进行序列化了。
Path 类序列化的原理就是通过将 path 绘制的每一个点都保存下来,需要还原的时候就进行反序列化,再通过这些保存的点重新绘制 path。
继承 android.graphics.Path 类,重写 moveTo, lineTo 等方法,记录下 path 绘制的每一点的坐标数据;反序列化的时候调用 “drawThisPath” 重绘 path。
相关代码:
public class CustomPath extends Path implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5974912367682897467L;
private ArrayList<PathAction> actions = new ArrayList<CustomPath.PathAction>();
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{
in.defaultReadObject();
drawThisPath();
}
@Override
public void moveTo(float x, float y) {
actions.add(new ActionMove(x, y));
super.moveTo(x, y);
}
@Override
public void lineTo(float x, float y){
actions.add(new ActionLine(x, y));
super.lineTo(x, y);
}
private void drawThisPath(){
for(PathAction p : actions){
if(p.getType().equals(PathActionType.MOVE_TO)){
super.moveTo(p.getX(), p.getY());
} else if(p.getType().equals(PathActionType.LINE_TO)){
super.lineTo(p.getX(), p.getY());
}
}
}
public interface PathAction {
public enum PathActionType {LINE_TO,MOVE_TO};
public PathActionType getType();
public float getX();
public float getY();
}
public class ActionMove implements PathAction, Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -7198142191254133295L;
private float x,y;
public ActionMove(float x, float y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public PathActionType getType() {
return PathActionType.MOVE_TO;
}
@Override
public float getX() {
return x;
}
@Override
public float getY() {
return y;
}
}
public class ActionLine implements PathAction, Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8307137961494172589L;
private float x,y;
public ActionLine(float x, float y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public PathActionType getType() {
return PathActionType.LINE_TO;
}
@Override
public float getX() {
return x;
}
@Override
public float getY() {
return y;
}
}
}
创建 PathInfo 类,方法 lineStart, lineMove, lineEnd 专门用来保存 path 绘制的每一个点的坐标数据;反序列化的时候重绘 path。原理跟实例1差不多。
之前在 Android adb 网络连接 中总结了一次 adb 的网络连接,而最近工作中遇到 Android 设备连接 adb 的时候出现 offline 的提示,无法正常连接上设备,这个情况应该如何解决呢?
这里总结一下解决方案:
如果这个能帮到你,请留言告诉我。
理论学习了 Android Path 类之后,对 Path 类的属性方法都有所了解,写两个例子实践一下。理论与实践结合嘛。
实例1,五环 + 文字:
源码:
package com.example.pathstudy;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Path;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
public class PathStudyActivity extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(new PathStudyView(getApplicationContext()));
}
private class PathStudyView extends View {
public PathStudyView(Context context) {
super(context);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// super.onDraw(canvas);
canvas.drawColor(Color.WHITE);
Paint mPaint = new Paint();
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(20);
int originX = 0;
int originY = 0;
int offsetX = 0;
int offsetY = 0;
int offsetLengthX = 240;
int offsetLengthY = 110;
float circleX = 150;
float circleY = 200;
float radius = 100;
// first circle
mPaint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
Path mPath = new Path();
mPath.addPath(getDrawCirclePath(circleX, circleY, radius));
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPaint);
// second circle
mPaint.setColor(Color.BLACK);
canvas.save();
offsetX = originX + offsetLengthX;
canvas.translate(offsetX, offsetY);
mPath.reset();
mPath.addPath(getDrawCirclePath(circleX, circleY, radius));
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPaint);
canvas.restore();
// thid circle
mPaint.setColor(Color.RED);
canvas.save();
offsetX += offsetLengthX;
canvas.translate(offsetX, offsetY);
mPath.reset();
mPath.addPath(getDrawCirclePath(circleX, circleY, radius));
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPaint);
canvas.restore();
// forth circle
mPaint.setColor(Color.YELLOW);
canvas.save();
offsetX = originX + offsetLengthX / 2;
offsetY = originY + offsetLengthY;
canvas.translate(offsetX, offsetY);
mPath.reset();
mPath.addPath(getDrawCirclePath(circleX, circleY, radius));
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPaint);
canvas.restore();
// fifth circle
mPaint.setColor(Color.GREEN);
canvas.save();
offsetX += offsetLengthX;
canvas.translate(offsetX, offsetY);
mPath.reset();
mPath.addPath(getDrawCirclePath(circleX, circleY, radius));
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPaint);
canvas.restore();
// draw text kevinems.com
// fifth circle
mPaint.setColor(Color.BLACK);
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
mPaint.setTextSize(100);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(5);
String websiteStr = "kevinems.com";
canvas.drawText(websiteStr, 110, 500, mPaint);
canvas.restore();
}
private Path getDrawCirclePath(float x, float y, float radius) {
Path mPath = new Path();
mPath.setFillType(Path.FillType.EVEN_ODD);
mPath.addCircle(x, y, radius, Path.Direction.CCW);
return mPath;
}
}
}
实例2,可以随意绘画 path 的手写板:
源码:
package com.example.view;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Path;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
public class PathView extends View {
private static final String LOG_TAG = "PathView";
private Path mPath;
private Paint mPaint;
private float mPosX;
private float mPosY;
public PathView(Context context) {
super(context);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
init();
}
private void init() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
mPath = new Path();
mPaint = new Paint();
mPaint.setColor(Color.GREEN);
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(5);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// super.onDraw(canvas);
Log.i(LOG_TAG, "onDraw");
canvas.drawColor(Color.WHITE);
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPaint);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// return super.onTouchEvent(event);
int action = event.getAction();
float x = event.getX();
float y = event.getY();
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
mPath.moveTo(x, y);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
mPath.quadTo(mPosX, mPosY, x, y);
invalidate();
break;
default:
break;
}
mPosX = x;
mPosY = y;
return true;
}
}
这是 Kevin 的一篇 Google Android API 的翻译习作,原文请移步:
public class
公共类
extends Object
继承 Object
| java.lang.Object | |
| ↳ | android.graphics.Path |
The Path class encapsulates compound (multiple contour) geometric paths consisting of straight line segments, quadratic curves, and cubic curves. It can be drawn with canvas.drawPath(path, paint), either filled or stroked (based on the paint’s Style), or it can be used for clipping or to draw text on a path.
Path类封装了由直线段,二次曲线,三次曲线混合(多轮廓)组成的几何路径。它可以通过 canvas.drawPath(path, paint) 进行绘制,包括填充和描边(取决于 paint’s Style 这个参数),或者它可以用于裁剪或绘制路径上的文本。
| Nested Classes 嵌套类 |
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| enum | Path.Direction | Specifies how closed shapes (e.g. rects, ovals) are oriented when they are added to a path. 指定封闭的形状(如矩形的,椭圆形),当它们被添加到路径时的方向。有顺时针和逆时针两个数值。 |
|||||||||
| enum | Path.FillType | Enum for the ways a path may be filled 填充方式的枚举类型:Path.FillType EVEN_ODD,用奇偶规则填充 Path.FillType INVERSE_EVEN_ODD,顾名思义,和EVEN_ODD规则恰好相反。 Path.FillType INVERSE_WINDING,同样,WINDING的反效果。 Path.FillType WINDING,用非零环绕数规则填充。 |
|||||||||
| Public Constructors 公共构造函数 |
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Path()
Create an empty path
创建一个空的 path |
|||||||||||
| Path(Path src)
Create a new path, copying the contents from the src path.
复制 Path src 到一个新的 path
|
|||||||||||
| Public Methods 公共类 |
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| void | addArc(RectF oval, float startAngle, float sweepAngle)
Add the specified arc to the path as a new contour.
将一个指定的弧形作为新的轮廓添加到 path
|
||||||||||
| void | addCircle(float x, float y, float radius, Path.Direction dir)
Add a closed circle contour to the path
添加一个闭合圆形轮廓到 path
|
||||||||||
| void | addOval(RectF oval, Path.Direction dir)
Add a closed oval contour to the path
添加一个闭合的椭圆形轮廓到 path
|
||||||||||
| void | addPath(Path src, float dx, float dy)
Add a copy of src to the path, offset by (dx,dy)
将源 path 拷贝一份并添加到 path(当前),dx, dy 为偏移
|
||||||||||
| void | addPath(Path src)
Add a copy of src to the path
将源 path 拷贝一份并添加到 path(当前)
|
||||||||||
| void | addPath(Path src, Matrix matrix)
Add a copy of src to the path, transformed by matrix
将源 path 拷贝一份并添加到 path(当前),由 matrix 进行转换
|
||||||||||
| void | addRect(float left, float top, float right, float bottom, Path.Direction dir)
Add a closed rectangle contour to the path
添加一个闭合的矩形轮廓到 path
|
||||||||||
| void | addRect(RectF rect, Path.Direction dir)
Add a closed rectangle contour to the path
添加一个闭合的矩形轮廓到 path
|
||||||||||
| void | addRoundRect(RectF rect, float[] radii, Path.Direction dir)
Add a closed round-rectangle contour to the path.
添加一个闭合的圆角矩形轮廓到 path
|
||||||||||
| void | addRoundRect(RectF rect, float rx, float ry, Path.Direction dir)
Add a closed round-rectangle contour to the path
添加一个闭合的圆角矩形轮廓到 path
|
||||||||||
| void | arcTo(RectF oval, float startAngle, float sweepAngle)
Append the specified arc to the path as a new contour.
追加指定的弧形到 path 作为一个新的轮廓
|
||||||||||
| void | arcTo(RectF oval, float startAngle, float sweepAngle, boolean forceMoveTo)
Append the specified arc to the path as a new contour.
追加指定的弧形到 path 作为一个新的轮廓
|
||||||||||
| void | close()
Close the current contour.
闭合当前轮廓
|
||||||||||
| void | computeBounds(RectF bounds, boolean exact)
Compute the bounds of the control points of the path, and write the answer into bounds.
计算路径的控制点的边界,并把答案写进边界
|
||||||||||
| void | cubicTo(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, float x3, float y3)
Add a cubic bezier from the last point, approaching control points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2), and ending at (x3,y3).
从上一个点添加一个三次贝塞尔曲线,经过控制点(x1, y1), (x2, y2),在(x3, y3) 结束
|
||||||||||
| Path.FillType | getFillType()
Return the path’s fill type.
返回 path 的填充类型
|
||||||||||
| void | incReserve(int extraPtCount)
Hint to the path to prepare for adding more points.
对 path 暗示将会添加更多的点
|
||||||||||
| boolean | isEmpty()
Returns true if the path is empty (contains no lines or curves)
当 path 为空时返回 true (包括没有线和曲线)
|
||||||||||
| boolean | isInverseFillType()
Returns true if the filltype is one of the INVERSE variants
如果填充类型为 INVERSE 变量的其中一种,返回 true
|
||||||||||
| boolean | isRect(RectF rect)
Returns true if the path specifies a rectangle.
如果 path 指定一个矩形,返回 true
|
||||||||||
| void | lineTo(float x, float y)
Add a line from the last point to the specified point (x,y).
从上一点到 (x, y) 画线
|
||||||||||
| void | moveTo(float x, float y)
Set the beginning of the next contour to the point (x,y).
将下一个轮廓的起点设置为 (x, y)
|
||||||||||
| void | offset(float dx, float dy, Path dst)
Offset the path by (dx,dy), returning true on success
将 path 偏移 (x, y),成功则返回 true
|
||||||||||
| void | offset(float dx, float dy)
Offset the path by (dx,dy), returning true on success
将 path 偏移 (x, y),成功则返回 true
|
||||||||||
| void | quadTo(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2)
Add a quadratic bezier from the last point, approaching control point (x1,y1), and ending at (x2,y2).
从上一个点添加一个二次贝塞尔曲线,经过控制点(x1, y1),在(x2, y2) 结束
|
||||||||||
| void | rCubicTo(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, float x3, float y3)
Same as cubicTo, but the coordinates are considered relative to the current point on this contour.
同 cublicTo,但坐标被认为是相对于当前轮廓上的当前点。
|
||||||||||
| void | rLineTo(float dx, float dy)
Same as lineTo, but the coordinates are considered relative to the last point on this contour.
同 lineTo,但坐标被认为是相对于当前轮廓上的上一点。
|
||||||||||
| void | rMoveTo(float dx, float dy)
Set the beginning of the next contour relative to the last point on the previous contour.
设置下一个轮廓的开始点相当于上一个轮廓的最后一点
|
||||||||||
| void | rQuadTo(float dx1, float dy1, float dx2, float dy2)
Same as quadTo, but the coordinates are considered relative to the last point on this contour.
同 quadTo,但坐标被认为是相对于当前轮廓上的上一点。
|
||||||||||
| void | reset()
Clear any lines and curves from the path, making it empty.
清空 path 里面的所有线和曲线
|
||||||||||
| void | rewind()
Rewinds the path: clears any lines and curves from the path but keeps the internal data structure for faster reuse.
清空 path 中的所有线和曲线,但是保留其内部数据以便快速重用
|
||||||||||
| void | set(Path src)
Replace the contents of this with the contents of src.
用源 path 代替当前 path 的内容
|
||||||||||
| void | setFillType(Path.FillType ft)
Set the path’s fill type.
设置 path 填充类型
|
||||||||||
| void | setLastPoint(float dx, float dy)
Sets the last point of the path.
设置 path 的最后一点
|
||||||||||
| void | toggleInverseFillType()
Toggles the INVERSE state of the filltype
切换 filltype 的逆状态
|
||||||||||
| void | transform(Matrix matrix, Path dst)
Transform the points in this path by matrix, and write the answer into dst.
应用矩阵变换当前 path, 并把结果写到目的 path
|
||||||||||
| void | transform(Matrix matrix)
Transform the points in this path by matrix.
应用矩阵变换当前 path
|
||||||||||
| Protected Methods 私有方法 |
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| void | finalize()
Invoked when the garbage collector has detected that this instance is no longer reachable.
当垃圾收集器检测到该实例不再可达时调用
|
||||||||||